Our approach
Departments of urology and nephrology at BOSH offer comprehensive diagnostic and treatment options for a wide range of conditions such as urinary incontinence, prostate and kidney cancers, kidney stones, male infertility, kidney dysfunction, kidney biopsy & dialysis. Combining excellent credentials and clinical experience BOSH emphasizes on minimally invasive treatments whenever appropriate.
Treatments at BOSH
Our Urologists provide the best service and care
for patients suffering from various related ailments and conditions.
Kidneys
Kidney Ultrasound
A kidney ultrasound is a non-invasive diagnostic exam, that produces images used to assess the size, shape, and location of the kidneys. Ultrasound can also be used to assess blood flow to the kidneys, detect cysts, kidney stones, and tumors. It is also the preferred method to evaluate a transplanted kidney.
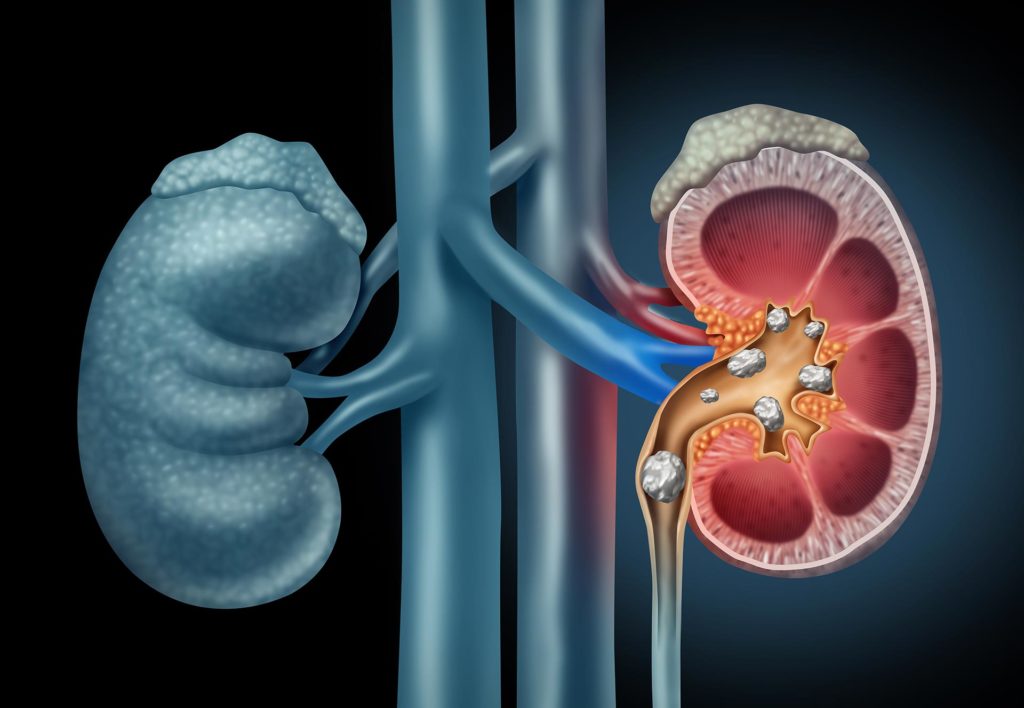
Kidney Stones
Hard deposits made up of minerals and salts are called kidney stones, often accompanied by symptoms like severe pain from the ribs to the lower abdomen and groin region, pain on urination, and persistent need to urinate. Treatment for small kidney stones involves managing pain through the administration of narcotics till the time of passing. In severe cases where the stones are large, a shock wave therapy called lithotripsy is performed, to break the kidney stone into smaller pieces allowing it to pass. People with large stones located in regions that do not allow for lithotripsy may receive surgical procedures for removal of the stone via an incision in the back or by inserting a thin tube into the urethra.
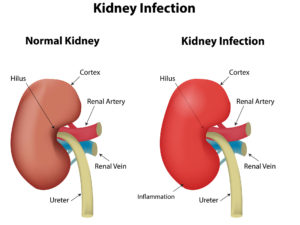
Kidney Infection
Kidney infection is a type of urinary tract infection (UTI) that generally begins in your urethra or bladder and travels to one or both kidneys. Symptoms could include fever, chills, back pain, abdominal pain, frequent urination, nausea, and vomiting. Caused by bacteria in most cases, kidney infection is predominantly treated with antibiotics.
Lower Abdomen
Urethral Stricture
Any inflammation of the urethra resulting from injury, trauma, previous surgery, or infection can cause urethral stricture. Symptoms of urethral stricture can range from no symptoms to complete urinary retention which can be diagnosed using imaging and endoscopic evaluations. Urethral dilation surgery is the recommended treatment for individuals with symptomatic urethral strictures.
Urinary incontinence
Urinary incontinence is a medical problem causing uncontrolled leakage of urine. This condition is known to affect the emotional, psychological, and social life of people suffering from it. The specialist in such cases recommends less invasive treatments to start with which may include behavioural training techniques, exercises to strengthen the pelvic floor, medications, and electrical simulations. In case further treatment is required, the specialist may advise the use of medical devices, interventional therapies, and finally surgery in case of menial improvement.
Bladder stones
Hard lumps of minerals that can form inside the bladder, called bladder stones, come with symptoms such as irritation in the wall of the bladder or blockage in the flow of urine. Surgery is usually needed to remove the stones from the bladder. The most common procedure is a cystolitholapaxy, where a thin tube (cystoscope) with a camera at the end is used to find the bladder stones. The cystoscope uses lasers or ultrasound to break up the stones before they are removed.
Genital Area
Treatment of erectile dysfunction
Diagnosis is critical for the treatment of erectile dysfunction that can be caused by trauma, medications, or psychological conditions. A thorough investigation followed by a frank conversation can lead to the best treatment plan customised to meet the patient’s needs. Oral medications, hormone supplements, surgery, and implants are some of the treatment modalities for this condition.
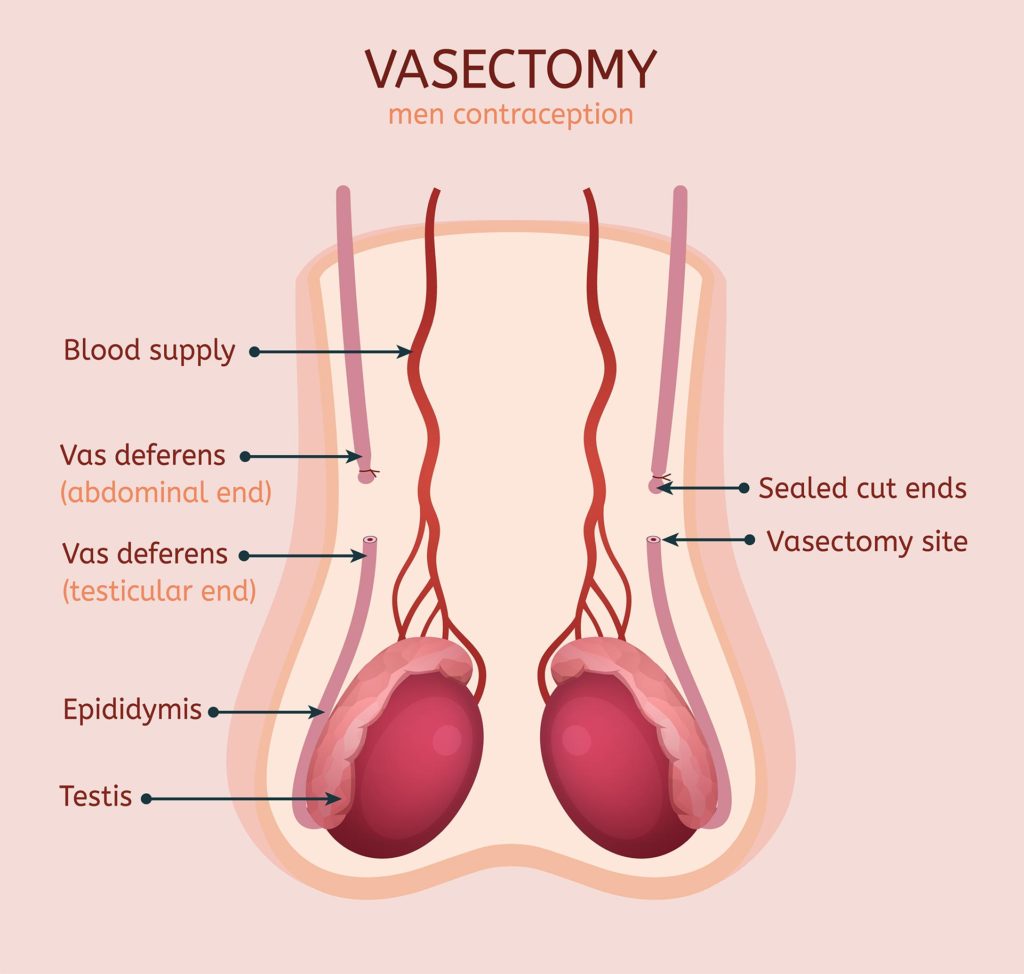
Vasectomy and Vasectomy Reversal
Vasectomy, a contraceptive surgery for men, is a minor operation wherein the tubes that carry sperm from a man’s testicles to the penis are cut, blocked, or sealed. This prevents the sperm from reaching the seminal fluid (semen) ejaculated from the penis during sex. There will be no sperm in the semen, so a woman’s egg can’t get fertilised. Vasectomy can be reversed and is known as vasectomy reversal surgery.
Circumcision
Male circumcision is the surgical removal of the foreskin, a retractable fold of skin that covers the end of the penis. This procedure is recommended in case of inflammation of the foreskin, or the inability to retract it. Circumcision is a relatively simple procedure. The foreskin is removed just behind the head of the penis using a scalpel or surgical scissors. A circumcision revision may be required in case of unsatisfactory results with the original circumcision.
Orchidopexy
Surgery to move an undescended testicle into the scrotum is called orchiopexy or orchidopexy. It is mostly performed on babies who are 9 to 15 months old. Depending on the location of the testicle, one or two small incisions are made in the scrotum, the groin, or the abdomen, to allow the surgeon to reach the testicle and move it to the scrotum. Placing undescended testicles in the scrotum may help prevent infertility and reduce the risk of testicular cancer.
Testicular Torsion
Testicular torsion occurs when a testicle rotates, twisting the spermatic cord that brings blood to the scrotum. The reduced blood flow causes sudden and often severe pain and swelling requiring emergency surgery. A small incision is made on the scrotum to untwist the cord which is bound by tiny sutures to keep the testicle in place, preventing rotation from occurring again.
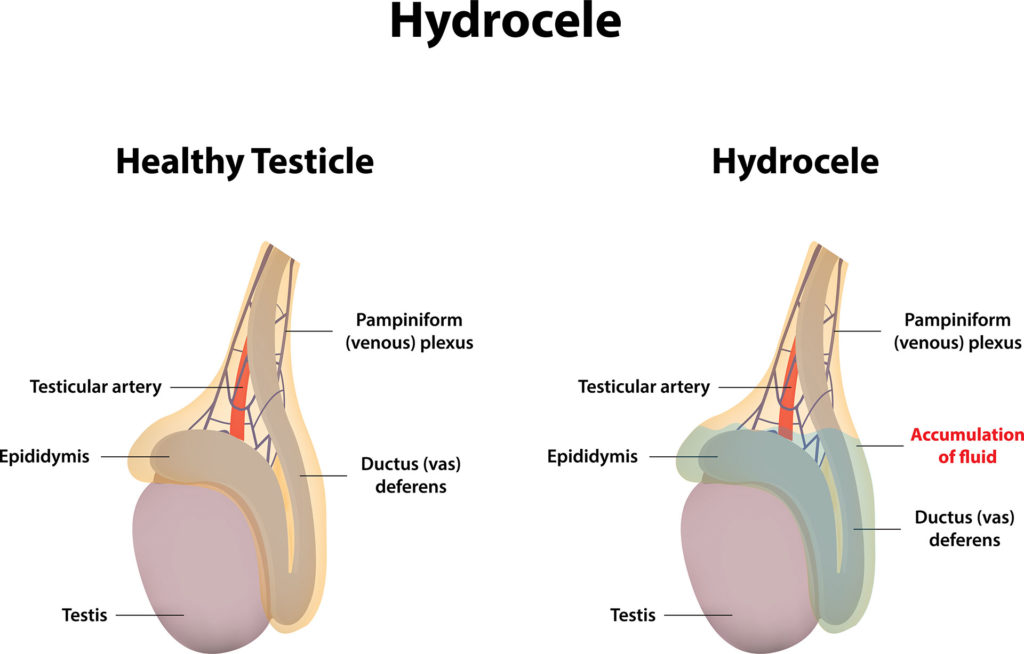
Adult hydrocele
A hydrocele is a build-up of watery clear fluid around one or both testicles which may be caused by trauma to the testes, infection or inflammation, and tumor of the testes. The signs and symptoms of the condition include swelling of the scrotum and groin and uncomfortable heaviness of the testicles. In most cases, treatment of an Adult Hydrocele may not be required, as the swelling usually subsides on its own. In a few cases, surgery may be recommended to drain the fluid.
Varicocele
A vein abnormality in the scrotum may result in a varicocele, an enlargement of the veins within the scrotum. A varicocele can result in decreased sperm production and quality, which in some cases can lead to infertility. Scrotal ultrasound is used to diagnose this condition. Based on the degree of discomfort, Varicocelectomy and varicocele embolization, which help blood flow to the normal veins, are the best courses of treatment.
Surgeries
Meatal Stenosis/ Meatotomy
Meatal stenosis is a common urologic complication post circumcision. Deviated urinary stream, difficult-to-aim, painful urination, and urinary frequency are common complaints of this condition. Meatotomy or meatoplasty is the definitive treatment for meatal stenosis. Meatotomy is a simple procedure in which the ventrum of the meatus is crushed for 60 seconds with a straight clamp and then divided with fine-tipped scissors.
Cystoscopy
Cytoscopy is a procedure conducted using a cystoscope – a thin tube with a camera and light on the end inserted through the urethra to visualize the inside of the bladder. Magnified images from the camera are displayed on a screen to help diagnose blockages, enlarged prostate gland, noncancerous growths, and problems with the ureters.
Ureteroscopy
It is a procedure in which a small scope (like a flexible telescope) is inserted into the bladder and ureter and it is used to diagnose and treat a variety of problems in the urinary tract. This is specifically used to find and remove urethral stones, hard lumps of minerals, which cause blockages and pain while passing urine.
Nephrectomy
Nephrectomy surgery is conducted to remove a diseased or cancerous kidney safely and effectively. Typically, This procedure is performed using a laparoscope. Laparoscopic surgery is a minimally invasive technique that has resulted in significantly less post-operative pain, a shorter hospital stay, an earlier return to work, a more favourable cosmetic result, and outcomes identical to that of open surgery.
Prostatectomy
A prostatectomy is a surgical procedure for the partial or complete removal of the prostate. This surgery is performed in case of prostate cancer or benign prostatic hyperplasia – a noncancerous enlargement of the prostate gland occurring in older men. Treatment includes surgical procedures like Laser therapy to remove part of your prostate or transurethral resection of the prostate, or TURP, in which the doctor uses a scope and cuts out pieces of the gland with a wire loop.
Nephrology
Kidney Biopsy
A kidney biopsy is conducted to identify a suspected kidney problem using a sample of kidney tissue. This tissue is then studied under a microscope to determine the extent of the damage. At BOSH, fluoroscopy (live X-ray) guides the needle to the precise location to get a quick and accurate result. The procedure takes about 30 minutes and does not require an overnight stay.
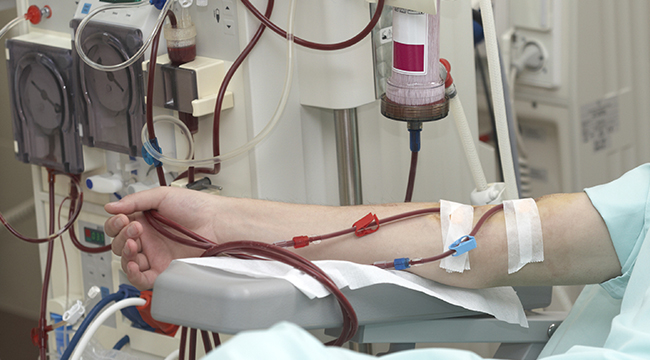
Dialysis
Chronic kidney diseases are treated through dialysis, which often involves using a machine to remove waste and extra fluids from the blood. Two types of dialysis can be recommended based on the diagnosis – peritoneal dialysis or Hemodialysis. Hemodialysis treatment requires the support of an artificial kidney machine to filter blood and requires visits to a dialysis centre. On the other hand, peritoneal dialysis uses the lining on the inside of the belly as a natural filter for blood and can be performed at home after sufficient training.
Our Specialists

Dr Kishore Babu